#NISAR #NASAISRO #EarthObservation #ClimateChange #SpaceResearch #IndoUSCollaboration #ISRO #NASA #EarthScience #GlacierMonitoring #AgricultureTech #SatelliteImagery
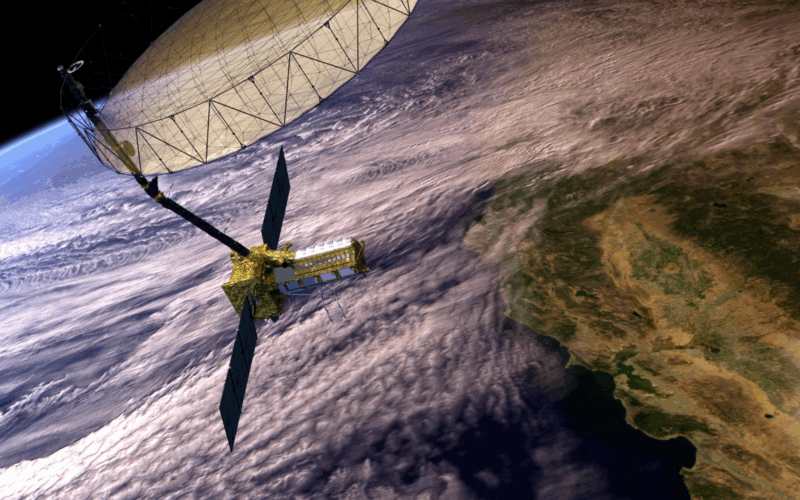
New Delhi/Washington: In a landmark collaboration that underscores the growing Indo-US space partnership, India’s ISRO and NASA have successfully launched the NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) satellite — the first radar imaging satellite designed to observe Earth’s land and ice surfaces in unprecedented detail.
The NISAR mission, jointly developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), aims to deliver high-resolution, all-weather, day-and-night global data on Earth’s natural processes, including shifts in glaciers, land subsidence, coastline erosion, and forest biomass.
🌍 What is NISAR?

NISAR is the world’s first dual-frequency radar imaging satellite, using both L-band and S-band synthetic aperture radar systems. It is designed to scan the entire globe every 12 days and monitor changes in the Earth’s surface with millimeter-level accuracy.
-
L-band radar: Developed by NASA, ideal for penetrating forest canopies and monitoring ice sheets and vegetation structure.
-
S-band radar: Developed by ISRO, particularly useful for tracking agricultural crops and urban infrastructure.
Together, the instruments make NISAR one of the most advanced Earth observation platforms ever built.
🚀 Launch and Orbit Details
-
Launch Date: July 30, 2025
-
Launch Vehicle: GSLV Mk II (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle)
-
Launch Site: Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, India
-
Orbit: Sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of approximately 747 kilometers
After an initial calibration and testing phase, NISAR will begin full-scale scientific operations in early 2026.
🌱 Why NISAR Matters
The satellite will track and analyze changes in Earth’s landmass, including:
-
Deforestation and forest biomass for climate change models
-
Glacier retreat and sea-level rise
-
Groundwater depletion and land subsidence
-
Earthquake zones and tectonic plate movements
-
Agricultural patterns and crop yield analysis
-
Urban sprawl and infrastructure monitoring
According to scientists, NISAR will generate nearly 85 terabytes of data per day, making it one of the richest datasets for Earth system science.
🤝 A Symbol of US-India Space Cooperation
The mission is a shining example of technological diplomacy. With joint funding and design, NISAR brings together NASA’s deep-space engineering capabilities and ISRO’s cost-effective satellite and launch expertise.
ISRO Chairman S. Somanath said:
“NISAR is not just a satellite; it’s a scientific leap in Earth observation and a celebration of Indo-US scientific partnership. It reflects our shared commitment to addressing climate challenges with data-driven decisions.”
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson echoed the sentiment:
“This is a historic milestone. NISAR will help humanity better understand our dynamic planet and equip policymakers, researchers, and communities with vital information to respond to global environmental changes.”
📡 Applications Across Sectors
The data from NISAR will be freely available to global users, including scientists, governments, disaster management authorities, and even private industries. Sectors expected to benefit include:
-
Agriculture – for crop health monitoring and yield prediction
-
Water Resources – mapping groundwater and surface water bodies
-
Urban Planning – tracking infrastructure development and land use
-
Disaster Management – real-time data on floods, earthquakes, and landslides
-
Climate Research – understanding carbon cycles and forest carbon stocks
🛰 Technical Highlights
-
Mass: 2,800 kilograms
-
Power: 5,000 watts via solar panels
-
Lifetime: Minimum 3 years of operations
-
Data Downlink: Via NASA’s Deep Space Network and ISRO ground stations
The mission architecture includes cloud-based data processing tools and machine learning support to convert raw data into actionable insights quickly.
🌐 The Road Ahead
NISAR is expected to revolutionize the precision and frequency of Earth monitoring, helping the world respond more swiftly to the pressing issues of climate change, resource scarcity, and disaster preparedness.
Its success also sets the stage for future India-US joint missions, possibly extending to planetary exploration and deep-space research.
Hashtags:
#NISAR #NASAISRO #EarthObservation #ClimateChange #SpaceResearch #IndoUSCollaboration #ISRO #NASA #EarthScience #GlacierMonitoring #AgricultureTech #SatelliteImagery #EnvironmentalProtection #DisasterManagement #GlobalWarming #SustainableDevelopment